As the world transitions towards sustainable energy solutions, solar power is becoming an increasingly popular option for homeowners and businesses worldwide. The grid-tied inverter is one of the critical components that make solar power systems functional and efficient.
If you’re looking to understand how solar power systems interact with the electrical grid, a grid-tied inverter is at the heart of that connection. This article will break down how does a grid tie inverter work and its benefits in solar energy systems.

What is a Grid Tie Inverter?
A grid-tie inverter, often called a grid-connected inverter, is designed specifically for solar power systems connected to the public electricity grid. Its primary job is to convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity compatible with the power grid and home appliances.
But there’s more to it than just conversion. A grid tie inverter also ensures that the AC power is synchronized with the grid’s frequency, voltage, and phase, allowing solar energy to be seamlessly integrated into the grid.

Types of Grid Tie Inverter
There are different inverter types of grid tie inverters designed for various system sizes and applications. They include:
- String Inverters
These are the most common for residential and commercial solar systems. They connect multiple solar panels in a series (or “string”) to a single inverter. - Microinverters
Unlike string inverters, microinverters are attached to individual solar panels, allowing each panel to operate independently. This increases overall system efficiency, especially in shaded or partially obstructed areas.
Explore further Microinverter vs String Inverter for more information.
How Does a Grid Tie Inverter Work?
The grid tie inverter application is when the link between solar energy production and its integration with the power grid. Here’s how it works step by step:
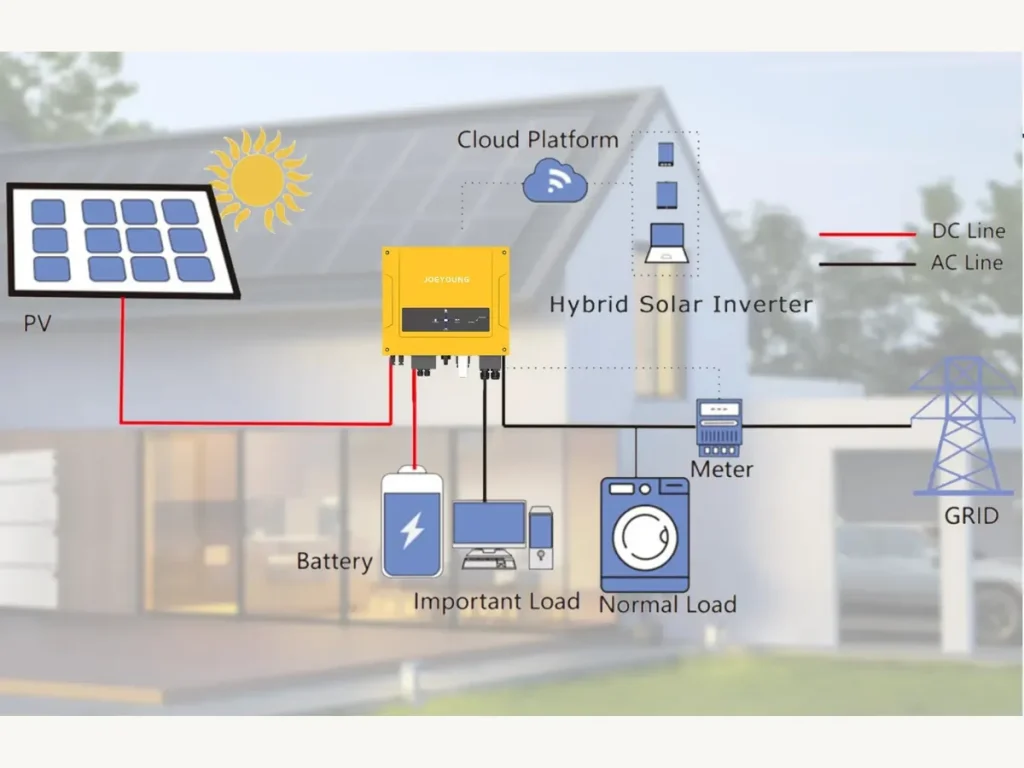
Solar Panels Generate DC Power
The process begins when sunlight hits the solar panels containing photovoltaic (PV) cells. These cells capture the sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. However, this DC electricity is unsuitable for most household appliances or the grid, which requires AC power.
Inverter Converts DC to AC
Once the solar panels generate DC power, it is sent to the grid-tied inverter. The inverter converts DC electricity into alternating current (AC) through inversion, where electronic components like transistors switch the DC flow at high speeds, generating AC output.
Synchronizing with the Grid
The real magic happens when the inverter synchronizes the AC output with the utility grid’s frequency, voltage, and phase. Power grids in most countries operate at a standard frequency (typically 50 Hz or 60 Hz), and the inverter must adjust the output power frequency to match that of the grid.
The inverter monitors the grid and adjusts the output power accordingly, ensuring that the electricity sent back to the grid is at the correct phase and voltage. This synchronization is crucial to prevent any power fluctuations, damage to the grid, or safety hazards.
Supplying Power to the Home or Business
Once the AC electricity is generated and synchronized, it can power electrical appliances in your home or business. The inverter will direct the electricity to your electrical system, ensuring that your home uses solar energy before drawing power from the grid.
Feeding Excess Power Back to the Grid
If your solar system generates more electricity than your home or business requires, the inverter will feed the excess power back into the electrical grid. This is where the concept of net metering comes into play. In many regions, utility companies allow solar users to return excess power to the grid in exchange for energy credits or compensation. This process is seamless and automatic, thanks to the grid tie inverter’s advanced technology.
Benefits of Using a Grid Tie Inverter
After understanding how a grid tie inverter works, let’s dive into the benefits of using a grid tie inverter. Here are some of the key benefits they provide:
Maximized Energy Usage
A grid-tie inverter ensures that all the electricity produced by the solar system is used efficiently, either for immediate consumption in your home or by sending surplus power back to the grid. This reduces wasted energy and maximizes the economic return of your solar investment, such as the Joeyoung Single-Phase Grid-tie Inverter.
Energy Independence and Cost Savings
Homeowners and businesses can reduce reliance on traditional energy sources by integrating solar power with the grid. This leads to lower electricity bills, and by feeding excess energy back into the grid, you can earn credits or financial compensation, further reducing costs.
Environmental Benefits
Grid-tied inverters help harness renewable energy from the sun, which is a clean, environmentally friendly power source. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, solar power systems with grid-tied inverters help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and the environmental impact of electricity generation.
Increased Grid Stability
Grid-tie inverters can improve the overall stability of the power grid. As more renewable energy sources, such as solar, are integrated into the grid, grid tie inverters help balance energy supply and demand, providing a more stable and sustainable energy system.
Low Maintenance
Grid-tie inverters typically require low inverter maintenance, with most systems requiring little attention after installation. With proper care and monitoring, they can function for many years with minimal intervention, making them a reliable component of solar energy systems.

Conclusion
In conclusion, a grid tie inverter is vital in operating solar energy systems connected to the public grid. By converting DC power to AC, synchronizing with the grid, and feeding excess energy back to the grid, grid tie inverters allow the users to benefit from solar energy while contributing to the stability of the power grid.
Plan your device with a trusted inverter manufacturer who can provide the ODM/OEM service tailored to your needs at an efficient cost.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, a grid tie inverter can work without battery storage. In fact, there is no battery backup in a standard grid-tied solar system; excess energy is sent to the grid. However, without storage, any excess power generated during the day is fed into the grid, and the homeowner cannot store it for nighttime use. This is where hybrid solar systems with battery storage provide an advantage, allowing the homeowner to use stored solar energy when sunlight is unavailable.
When a solar system produces more electricity than a household needs, the grid tie inverter sends the excess power to the electrical grid. This process is known as net metering, where surplus power is exported back to the grid, often earning the system owner energy credits or financial compensation. This helps optimize the use of the solar system and provides a way to "store" energy for later use without needing a battery system.
A standard grid tie inverter cannot provide power during a power outage because it is designed to shut down when it detects a loss of grid power. This safety feature prevents the inverter from sending power to the grid when workers are repairing electrical lines. However, hybrid systems with battery storage or backup systems can be designed to keep the solar system running during an outage. In such setups, the inverter switches to “island mode” and draws power from the battery storage to power the home.
The typical lifespan of a grid tie inverter is around 10 to 15 years, although some high-quality models can last longer with proper maintenance. Inverters generally require little maintenance but need occasional monitoring to ensure they are functioning correctly. Over time, however, inverters may need to be replaced as their efficiency diminishes, especially if they experience issues like overheating or component wear. It’s recommended to check warranty conditions and consider the cost of replacement when investing in an inverter.

Regarding solar power utilisation, several inverter types may be an option, but what is a string inverter? Why can it be the perfect match to optimize the solar systems? This article will give you the information that you need.

This article will dive into the role of IGBT and MOSFET inverters, the pros and cons, and each distinct characteristic.

This article answer the question “what can I run on a 2000-Watt inverter?” and several important information.
Authors

Passionate to education and renewables energy make me enthusiast about making complex technologies accessible to everyone by translating it into a practical and easy to understand. Let's learn and grow together!
View all posts

hi I am Jim, an inverter specialist with over 10 years of experience. I previously worked as an R&D engineer at a leading energy company, focusing on inverter design, optimization, and system integration. I have been involved in the development of key technologies and gained comprehensive expertise in both technical innovation and practical applications.Currently, I focus on professional writing to provide clear analysis and practical insights into inverter technology, contributing to its advancement and broader adoption in the industry.
View all posts